Publication highlights
Hans Kroha co-authors a Nature Physics article on quantum phase transitions
Hans Kroha co-authors a Nature Physics article on quantum phase transitions [according to the press release of the University of Bonn] Many substances change their properties when they are cooled below a certain critical temperature. Such a phase...
Preprint from Ando group recommended in the Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics
Preprint from Ando group recommended in the Journal Club for Condensed Matter Physics The preprint entitled "Induced superconducting correlations in the quantum anomalous hall insulator" by Anjana Uday et al. was recommended for discussion in the Journal Club for...
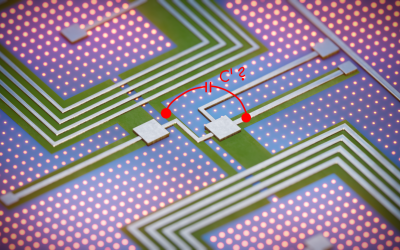
New work on quantum dynamics of regularized superconducting circuits
New work on quantum dynamics of regularized superconducting circuits Building a universal quantum computer is a challenging task because physical quantum bits, or qubits, are imperfect. The pursuit of novel qubit designs, which strive for tailored...
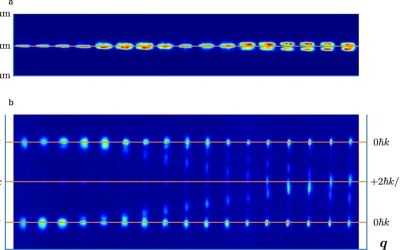
Joint work on chaos aspects of quantum computers continues
We reported one year ago about the successful research conducted in the ML4Q groups of Simon Trebst, Alex Altland and David DiVincenzo which analyzed cutting edge device structures to demonstrate that some of them are indeed operating dangerously close to a...
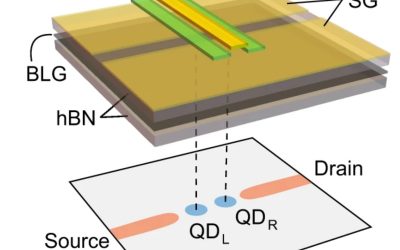
Exciting bilayer graphene characteristics published in Nature
Near perfect particle-hole symmetry in graphene quantum dots Researchers at RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich have uncovered important characteristics of double quantum dots in bilayer graphene, an increasingly promising material for possible...
Cross-Site Paper on Statistical Majorana Bound State Spectroscopy
Cross-Site Paper on Statistical Majorana Bound State Spectroscopy The groups of Fabian Hassler (RWTH) and Reinhold Egger (HHU Düsseldorf) have been cooperating on several projects to theoretically investigate signatures of Majorana zero modes that are...
Publication in Nature Communications on quantum Rabi dynamics of trapped atoms
In a collaboration with Enrique Rico and Enrique Solano (Department of Physical Chemistry, University of the Basque Country), Martin Weitz recently published the work of his group on quantum Rabi dynamics of trapped ions. The coupling of a two-level system with an...
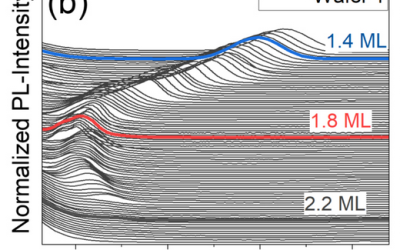
Study investigates Gallium deposition amount prior to In droplet epitaxy and its effect on the formation of a wetting layers in quantum dots
Work by the group of ML4Q member Beata Kardynal was recently published in Nanotechnology. The publication reports on results obtained in a study which investigates Gallium deposition amount prior to In droplet epitaxy and its effect on the formation of a wetting...
Work published in Physical Review Letters shows that fluctuations and response of a BEC to a bath of molecules are directly linked by thermal energy
Work by ML4Q Young Investigator Julian Schmitt and his team was recently published in Physical Review Letters. The discussed results show that fluctuations and response of a BEC to a bath of molecules are directly linked by thermal energy. The results demonstrate "the...
Study suggests a platform for the realization of fully in vacuo quasi-1D nanostructures of three dimensional topological insulators
Joint work of ML4Q members Mussler, Schüffelgen, Grützmacher, Schäpers and Mayer at Forschungszentrum Jülich was recently published in Nanomaterials. In the work, the authors introduce a platform that facilitates the realization of fully in vacuo quasi-1D...
Publication in Nanomaterials about electronic transport properties of a multi terminal Josephson junction
Joint work of ML4Q members Mussler, Schüffelgen, Grützmacher and Schäpers at Forschungszentrum Jülich was recently published in Nanomaterials. The publication reports on results obtained in a study of the properties of superconductivity induced into a topological...
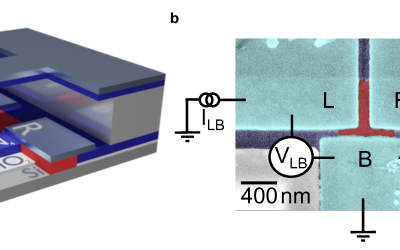
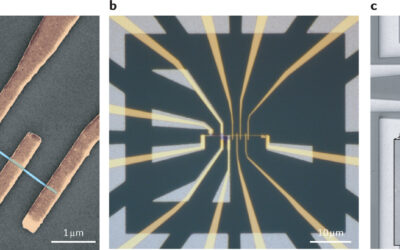
Schreiber and Bluhm group demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip
Lars Schreiber and Hendrik Bluhm have now come a significant step closer to solve qubit connectivity on semiconductor chips. Their team succeeded in transferring electrons, the carriers of quantum information, over several micrometres on a quantum chip. Their "quantum...
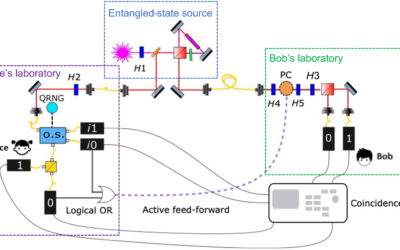
New insights into Quantum Conference Key Agreement by the Bruss group published in PRX Quantum
ML4Q researchers from Düsseldorf (Bruss group) have published a paper in PRX Quantum on Quantum Conference Key Agreement.Congratulations to all the authors on their impressive results! Publication Federico Grasselli, Gláucia Murta, Jarn de Jong, Frederik Hahn,...
Quantum computing breakthrough in error correction
Quantum computing breakthrough in error correction Researchers at ETH Zurich, supported by the Theoretical Quantum Technology Group at RWTH Aachen and Forschungszentrum Jülich as well as by colleagues in Canada, have succeeded, for the first time, in quickly and...
Error-Free Quantum Computing gets real – Fundamental building blocks for fault-tolerant quantum computing demonstrated
Error-free quantum computing gets real Fundamental building blocks for fault-tolerant quantum computing demonstrated For quantum computers to be useful in practice, errors must be detected and corrected. A research group at RWTH Aachen University, in...
Quantum one-way street in topological insulator nanowires
Quantum one-way street in topological insulator nanowires Very thin wires made of a topological insulator could enable highly stable qubits, the building blocks of future quantum computers. Scientists see a new result in topological insulator devices as an important...
Quantum Computing challenged by disorder – study published in Nature Communications
Research conducted in the ML4Q groups of Simon Trebst, Alex Altland and David DiVincenzo analyzed cutting edge device structures to demonstrate that some of them are indeed operating dangerously close to a threshold of chaotic meltdown. The challenge is to walk a thin...
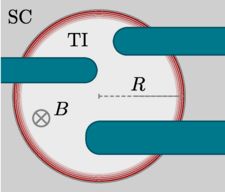
First Hybrid Quantum Bit Based on Topological Insulators
First Hybrid Quantum Bit Based on Topological Insulators Scientists at Forschungszentrum Jülich take an important step on the path towards topological quantum computers With their superior properties, topological qubits could help achieve a...
Realization of proximity-induced superconductivity in a topological-insulator nanowire
The Ando group has developed a new methodology to realize proximity-induced superconductivity in a topological-insulator nanowire. The work was conducted in cooperation with the Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons at Forschungszentrum...
2D materials for next generation computing
In a compact comment published in Nature Communications, Max Lemme, Christoph Stampfer and colleagues outline the most promising fields of applications of two-dimensional (2D) materials, as well as the challenges that still need to be solved to see the appearance of...
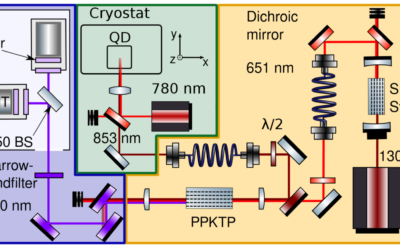
Inter-site collaboration demonstrates wavelength conversion of single photons emitted by semiconductor quantum dots
Inter-site collaboration demonstrates wavelength conversion of single photons emitted by semiconductor quantum dots ML4Q researchers from Bonn and Jülich have published recent results in Optics Letters on wavelength conversion at the single-photon level - a...
Extremely compressible “gas of light”
Busley et al. bring these advantages to quantum gases of light and explore a textbook scenario: a two-dimensional, spatially uniform gas of bosons.[from Photons think inside the box, Perspective, Science 375 (6586), pp. 1355-1356, 2022]The group of Martin Weitz...
Observing the difference between quantum and classical causality
In an international multi-site cooperation, scientists from the ML4Q Cluster of Excellence are able to observe quantum effects in cause and effect relationship in a photonic experiment. Understanding causal relationships in the observed data is a deeply rooted concept...
Nature Reviews Physics: Oliver Breunig and Yoichi Ando review opportunities of topological insulator devices
Topological insulators hold promise as a platform for unique quantum phenomena. However, realizing these phenomena experimentally requires sophisticated devices. In a Technical Review in Nature Reviews Physics, ML4Q spokesperson Yoichi Ando and ML4Q associated member...
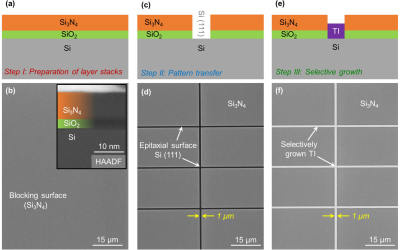
New insights in thin topological insulator films published in Advanced Quantum Technologies
Several scientists around ML4Q members, Bert Voigtländer, Stefan Tautz and Detlev Grützmacher, at Forschungszentrum Jülich have succeeded in taking an important step towards the realization of novel electronic components. Using a special four-tip scanning tunneling...
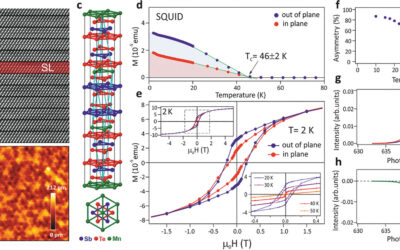
Topologically interesting through a bit more of Manganese – new publication in Advanced Materials
In a coordinated work with Gunther Springholz (Johannes Kepler University, Austria) and Oliver Rader (Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin for Materials and Energy), ML4Q member Markus Morgenstern at RWTH Aachen published the results of recent work on ferromagnetic topological...
New publication in Physical Review X by the Diehl group
Effective Theory for the Measurement-Induced Phase Transition of Dirac Fermions The recent discovery of a novel type of phase transition - driven by the competition between a quantum system’s internal evolution and its external observation - has sparked significant...
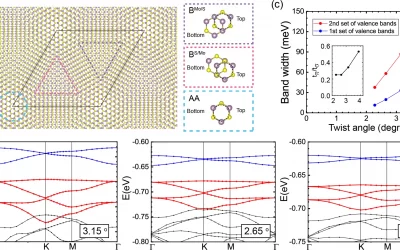
Results of joint work between the Kennes and Trebst groups published in Nature Communication
ML4Q researchers from Aachen (Kennes group) and Cologne (Trebst group) have published with colleagues from Hamburg and the US a Nature Communications paper on the collective behavior of twisted bilayer MoS2 in the presence of interactions. In the study, the authors...
New paper in Quantum Science and Technology
In their recent publication, David DiVincenzo and Cica Gustiani report on new findings concering blind oracular quantum computation (BOQC) schemes. They present an optimized BOQC scheme which possesses the same security as BOQC and is runnable with minimal physical...
New publication: Spin-valley coupling in single-electron bilayer graphene quantum dots
The 2D Materials and Quantum Devices Group published new results on low-energy single-electron spectra in bilayer graphene quantum dots. Publication: Banszerus, L., Möller, S., Steiner, C. et al. Spin-valley coupling in single-electron bilayer graphene quantum dots....