© ARQUE Systems GmbH
Technology
Transfer
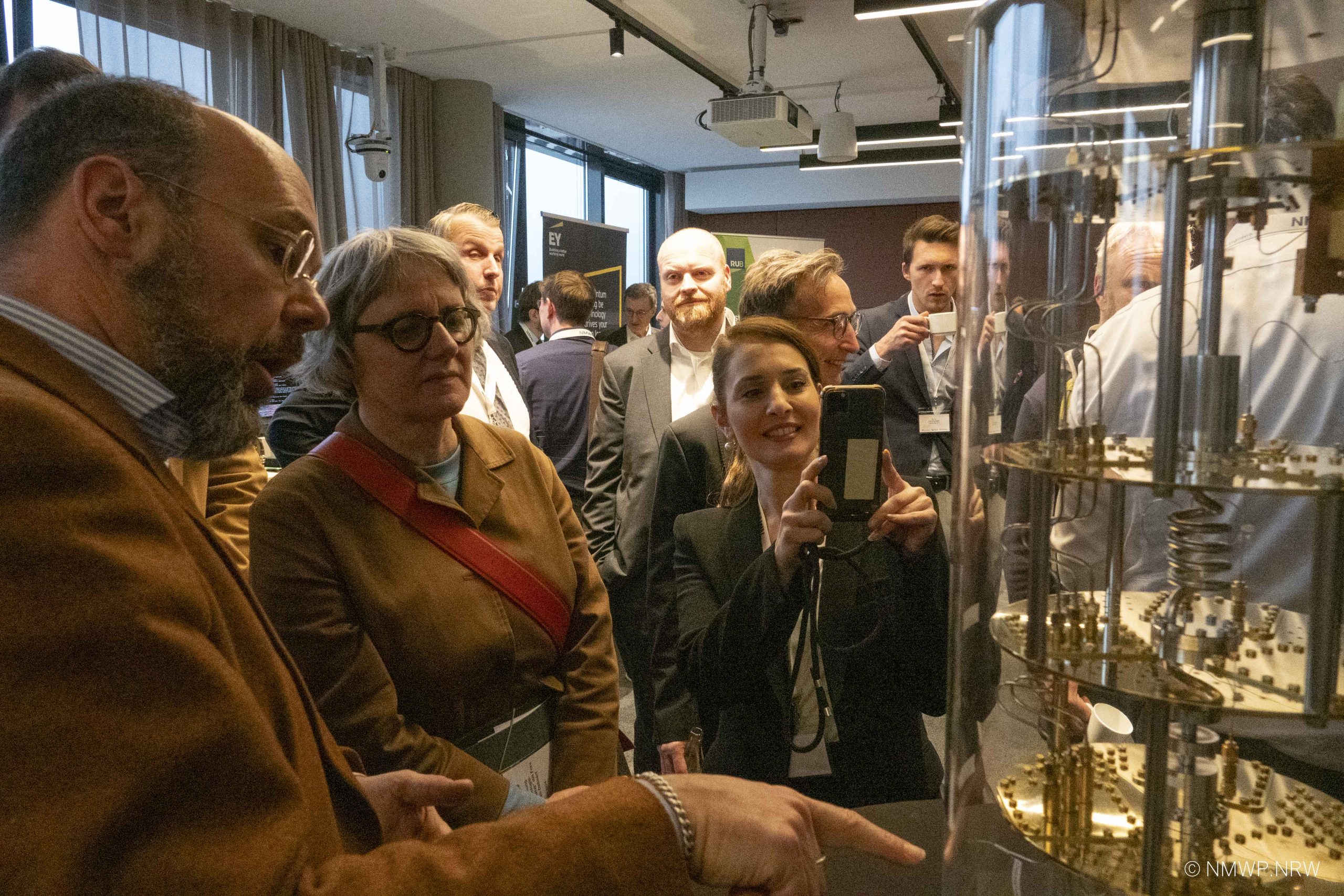
ML4Q has been playing an important role in shaping the State of NRW in general and, specifically, the Rheinland region into a hub for quantum technology, with fundamental research serving as the foundation for its transfer activities. Building on this research, the cluster supports early-stage projects and startup ventures, facilitating collaborations with industry partners and driving the commercialization of quantum innovations.
© Lars Schreiber
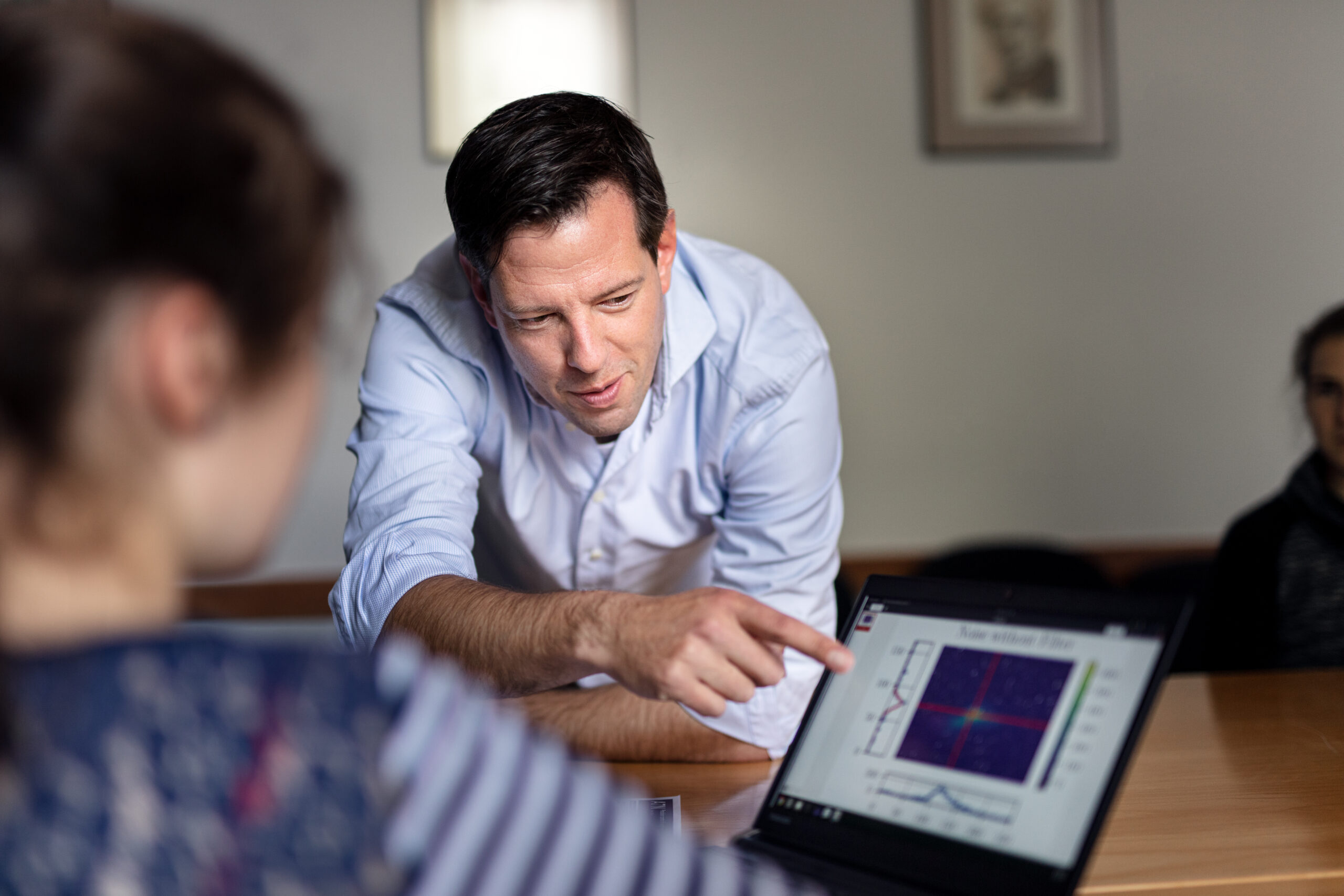
Projects
ML4Q funds projects at an early technology readiness level. In addition, ML4Q Members are leading several application-oriented projects and a number of industry-academia consortia co-funded by the federal government.
© Magda Baer Radermacher
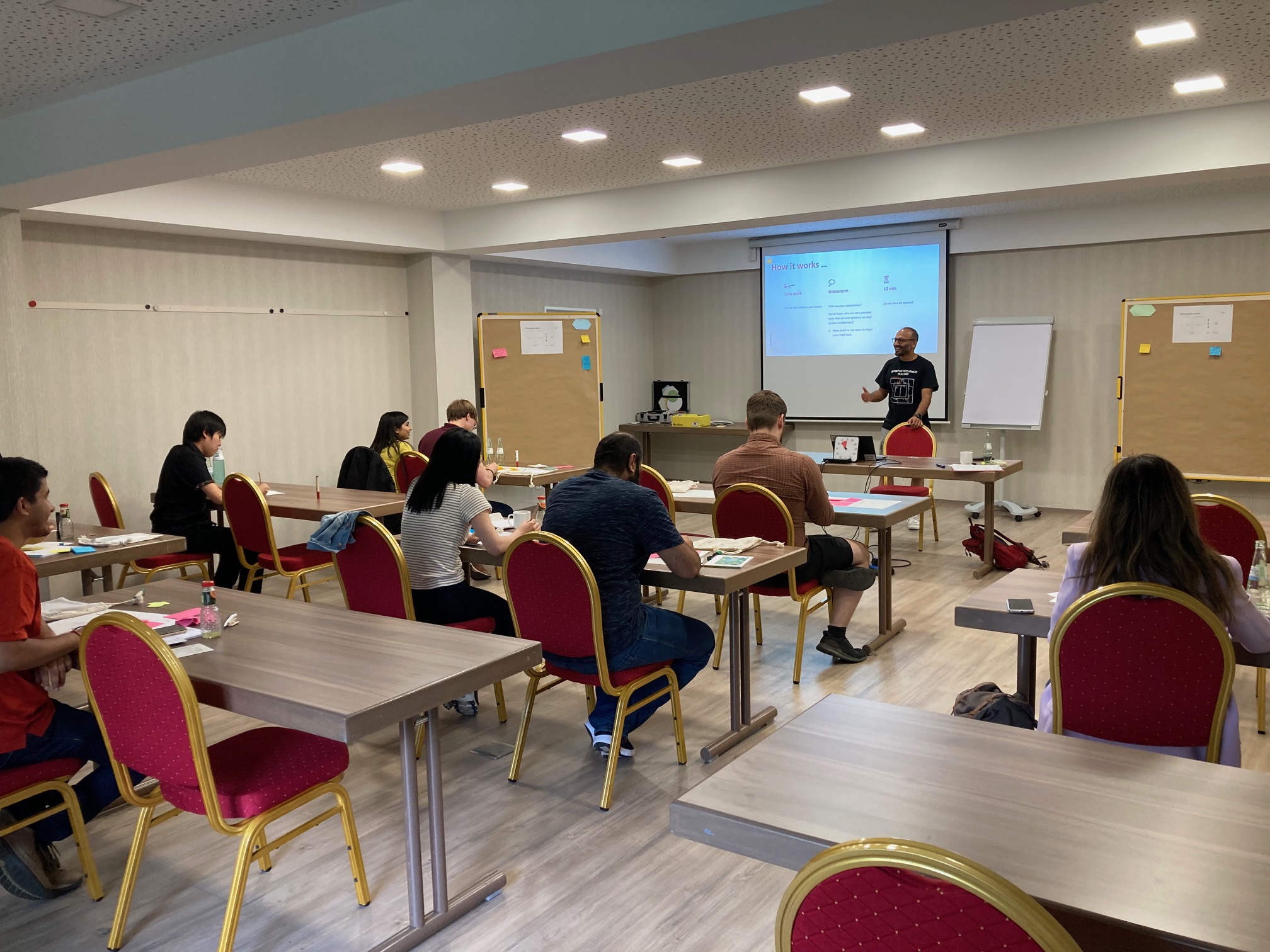
Workshops
To facilitate connections between early-career scientists and industry experts, we host the ML4Q Technology Day and other workshops on intellectual property rights and entrepreneurial thinking.
© Midel Photonics GmbH
Spinoffs
Spinoffs of the ML4Q community are now commercializing laser beam-forming components (Midel Photonics GmbH), rapid characterisation technologies to guide the design of next-generation devices (qruise GmbH) and quantum computing architectures based on electron spins in silicon (ARQUE Systems GmbH).
Technology
Transfer News
Other studies
Two studies have been conducted at Forschungszentrum Jülich as part of the knowledge transfer activities of the PGI-12. In the first study, small and medium-sized enterprises, rather than larger companies which cooperate with the Forschungszentrum, were interviewed in order to evaluate how they can be involved in the development of components and algorithms or software. Daniel Zeuch, leader of the study, elaborates on the genesis of this study and its main findings in this interview, titled “How quantum-ready are German companies?”. The other study, conducted by the Federal Office for Information Security, discusses the current state of affairs in the theoretical aspects and physical implementation of quantum computing, with a focus on applications in cryptanalysis. It is designed to be an orientation for scientists with a connection to one of the fields involved—such as mathematicians, computer scientists.
Quantum Computing for SMEs
Status of quantum computer development
Projects
ML4Q funds projects at an early technology readiness level that include joint Ph.D. students with high-tech industry partners, such as Covestro AG (quantum chemistry simulations) and Infineon Technologies AG (electron shuttling project).
Together with researchers from Covestro, we are working on quantum algorithms for chemistry problems, in particular with an eye on near-term “noisy intermediate-scale quantum computers” (NISQ). This work is conducted as a joint PhD project within the core project P3.2 and resulted in 2020 in a publication in Physical Review Research entitled “Avoiding local minima in variational quantum eigensolvers with the natural gradient optimizer”. The quantum computing team at Covestro (lead: Christian Gogolin, PhD) has grown further ever since and hosted three PhD students.
Papers emerging from this project include “Local, expressive, quantum-number-preserving VQE ansätze for fermionic systems” and “General parameter-shift rules for quantum gradients“
Building on ideas from core project P3.3, the JARA Institute for Quantum Information is coordinating a BMBF project on the realization of a shuttling-based scalable architecture. A key element of the project is to transfer the device fabrication concepts developed by the institute within ML4Q to industrial semiconductor technology at Infineon Dresden GmbH, Leibniz institute IHP and Fraunhofer IPMS. Discover more details on this project in the publication highlight “Bluhm and Schreiber groups demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip“.
Workshops
Through the establishment of EIN Quantum NRW, North Rhine-Westphalia joined forces to create a hub for quantum science and technologies in the region. In a joint effort with this initiative, the cluster launched in 2021 the annual ML4Q Technology Day offering early career associates a platform to connect with experts from the corporate world.
Together with the Gateway Exzellenz Start-up Center in Cologne the cluster offers an Intellectual Property Seminar as well as a workshop titled “Your Research Canvas – Pitch the Potential of Your Ideas” where early-career researchers are encouraged to view their projects from new perspectives to discover their application potential. They reflect on the user groups and stakeholders relevant to their research. Through brainstorming sessions, they collaborate to refine their ideas and explore potential use cases. The training also provides practical tips on delivering effective pitches. The workshops are led by certified Young Entrepreneurs in Science trainers from our universities’ transfer offices and are offered regulary at the annual Students and Postdocs retreats.
Spinoffs
![]()
In a remarkably effective Open Call project, David Dung, Frederik Wolf and Christian Wahl were successful in spinning-off methods used within Focus Area 4 to
produce laser beam-forming components for industrial purposes. The entrepreneurial team of Midel Photonics which combines scientific as well as business expertise
succeeded in securing seed funding from other programs including the High-Tech.NRW Start-Up Business Accelerator program and EXIST Research Transfer.
THE MIDEL PHOTONICS STORY
![]()
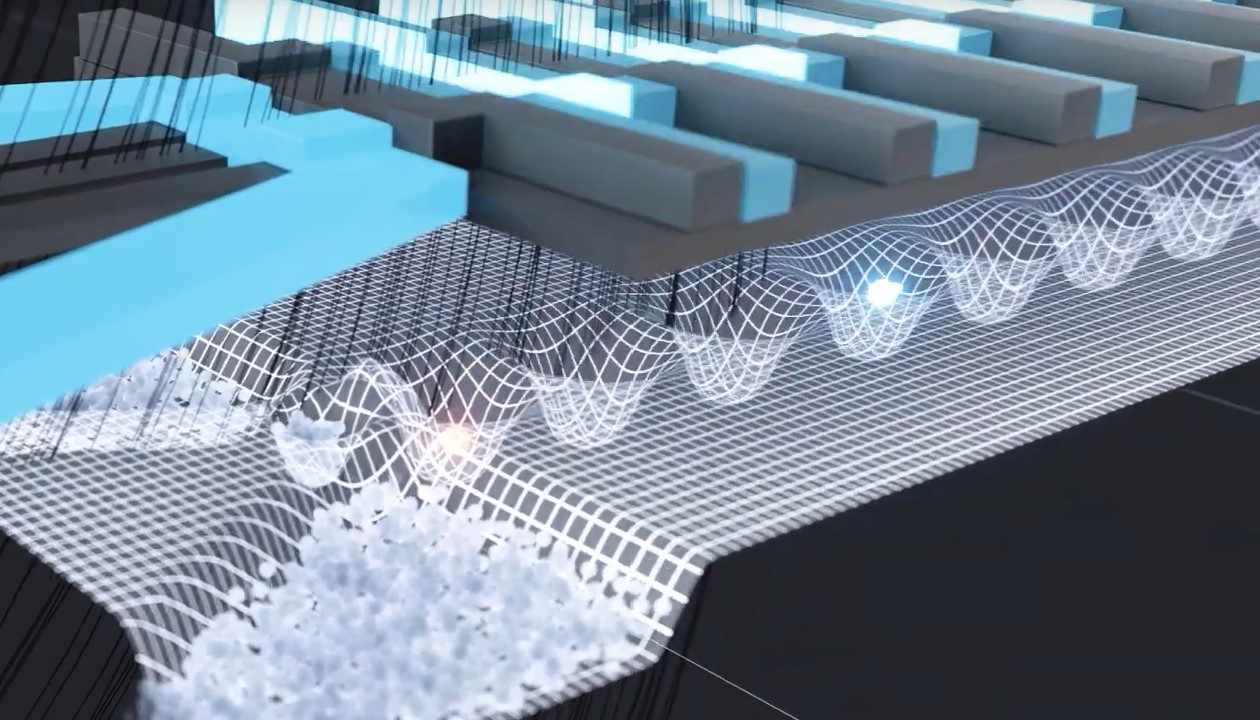
ARQUE Systems, a dynamic startup and a spin-off from RWTH Aachen University and the Forschungszentrum Jülich, embarked on its journey in 2022 to build fully scalable quantum computers using electron spins in silicon, leveraging a unique shuttling-based quantum computing unit. The story begins with ML4Q core project P3.3, where the team around Hendrik Bluhm laid the foundation for innovation. They successfully transferred the cutting-edge technology of electron spin shuttling with the help of the BMBF-project QUASAR to industrial semiconductor production lines at Infineon Dresden, effectively bridging the gap between academia and industry. Establishing a complete supply chain, ARQUE Systems now works with industry-grade quantum processing units, setting new standards in semiconductor quantum computing.
At the heart of ARQUE’s technology lies the concept of electron spin shuttling, a revolutionary approach that enables qubits with a mere 100 nm footprint to be transferred coherently across the entire quantum chip architecture on the micrometer scale. The increased space between neighboring qubits facilitates the integration of control electronics directly on the quantum chip, significantly reducing signal cross-talk and ensuring higher qubit fidelities, thus unlocking the true potential of quantum computing. With this approach, a quantum chip with the size of 1 cm 2 can host 1 million qubits without compromising their operation fidelities.

Another startup company which emerged within the ML4Q community is Qruise GmbH which develops a machine learning based toolkit to improve quantum devices and speed up research processes. The company was co-founded by ML4Q members Tommaso Calarco and Frank Wilhelm-Mauch.